Solar Energy vs. Traditional Electricity: What’s the Difference?
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, homeowners and businesses are increasingly considering sustainable power sources. One of the best starting points is understanding the basics of solar power.
I explain this in detail in my guide Solar Power Made Simple
Understanding the differences between these two options is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with your energy needs and environmental goals.
 The distinction between solar energy and traditional electricity lies in their sources and environmental impacts. While traditional electricity is often generated from fossil fuels, solar energy harnesses the power of the sun, providing a cleaner alternative. This fundamental difference affects not only the environment but also the cost and reliability of the energy supply.
The distinction between solar energy and traditional electricity lies in their sources and environmental impacts. While traditional electricity is often generated from fossil fuels, solar energy harnesses the power of the sun, providing a cleaner alternative. This fundamental difference affects not only the environment but also the cost and reliability of the energy supply.
👉 Want the Full beginner-friendly breakdown of solar savings, myths, and step-by-step adoption?
Read My guide 👉 Solar Power Made Simple
Key Takeaways
- Renewable energy sources like solar energy offer a cleaner alternative to traditional electricity.
- The choice between solar energy and traditional electricity impacts both the environment and energy costs.
- Sustainable power sources are becoming increasingly important for homeowners and businesses.
- Understanding the differences between energy sources is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
📑 Table of Contents
- Introduction: Solar Energy vs Traditional Electricity
- Understanding the Basics of Energy Generation
- 1.1 How Traditional Electricity is Generated
- 1.2 How Solar Energy Works
- 1.3 Key Fundamental Differences
- The Environmental Impact Comparison
- 2.1 Carbon Footprint of Traditional Electricity
- 2.2 Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
- 2.3 Long-term Environmental Considerations
- Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-term Savings
- 3.1 Upfront Costs of Solar Installation
- 3.2 Traditional Electricity Billing Structure
- 3.3 Return on Investment Timeline
- 3.4 Financial Incentives and Tax Credits
- Reliability and Consistency Factors
- 4.1 Weather Dependency of Solar Energy
- 4.2 Energy Storage Solutions
- How to Evaluate Your Home’s Solar Energy Potential
- 5.1 Roof Orientation and Shading
- 5.2 Local Climate Considerations
- 5.3 Space Requirements and Structural Factors
- 5.4 Local Regulations and HOA Restrictions
- Step-by-Step Guide to Transitioning to Solar Energy
- 6.1 Researching and Selecting Solar Installers
- 6.2 Understanding Proposals and Financing Options
- 6.3 Navigating Permits and Utility Agreements
- 6.4 Installation Process and Timeline
- Maintenance Requirements Comparison
- 7.1 Solar Panel Maintenance Schedule
- 7.2 Traditional Electrical System Upkeep
- 7.3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Grid Connection vs Off-Grid Solar Solutions
- 8.1 How Grid-Tied Systems Work (Net Metering)
- 8.2 Battery Storage Implementation
- 8.3 Complete Off-Grid System Requirements
- Making the Switch: Real-World Solar Energy Success Stories
- 9.1 Residential Case Studies
- 9.2 Common Challenges and Solutions
- 9.3 Unexpected Benefits for Homeowners
- Conclusion: Making the Right Energy Choice
- FAQ
1. Understanding the Basics of Energy Generation
As the world moves towards cleaner energy, understanding the basics of traditional electricity generation and solar energy becomes crucial. Traditional electricity generation involves various methods to produce power on a large scale.
1.1 How Traditional Electricity is Generated
Traditional electricity is generated through several primary methods.
Fossil Fuel Power Plants
Fossil fuel power plants burn coal, natural gas, or oil to produce electricity. These plants are significant contributors to global energy production but have environmental drawbacks.
Nuclear and Hydroelectric Sources
Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear reactions, offering a low-carbon alternative. Hydroelectric power plants harness the energy of moving water to produce electricity, representing another renewable energy source.
1.2 How Solar Energy Works
Solar energy works by converting sunlight into electricity.
The Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is the process by which solar panels convert sunlight into electrical energy. This effect occurs in semiconducting materials, which release electrons when exposed to sunlight.
Solar Panel Components
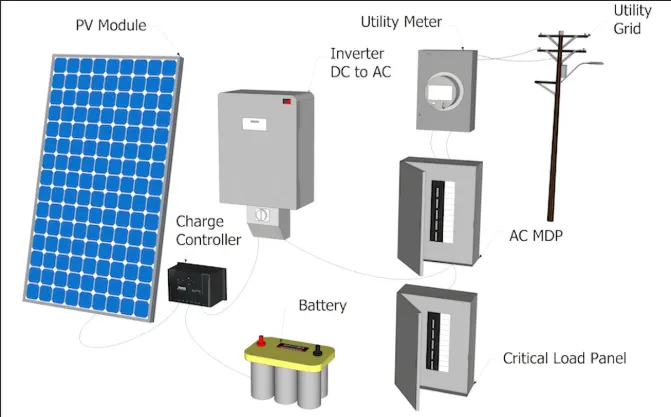
Solar panels are composed of photovoltaic cells, an inverter to convert DC power to AC, and a mounting system to secure the panels in place.
1.3 Key Fundamental Differences
The primary difference between traditional electricity generation and solar energy lies in their energy sources and environmental impact. Traditional methods often rely on finite resources and can have significant environmental consequences, whereas solar energy is renewable and cleaner.
2.The Environmental Impact Comparison
Comparing the environmental impact of traditional electricity and solar energy reveals stark contrasts in their ecological footprints. Traditional electricity generation, primarily through fossil fuels, has been a significant contributor to environmental degradation.
2.1 Carbon Footprint of Traditional Electricity
Traditional electricity generation is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, with coal and natural gas being substantial contributors to carbon dioxide emissions. The carbon footprint of traditional electricity is considerable, with the average American home consuming over 900 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per month, resulting in significant emissions.
2.2 Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
In contrast, solar energy offers a cleaner alternative, producing electricity without the direct emission of greenhouse gases. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a renewable energy source that mitigates climate change by reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
2.3 Long-term Environmental Considerations
While solar energy is environmentally friendly during operation, it's essential to consider the lifecycle impacts, including manufacturing and end-of-life phases.
Manufacturing Impact
The production of solar panels involves materials like silicon, aluminum, and silver, which require energy and resources. However, studies show that solar panels typically offset their manufacturing emissions within 1-3 years of operation.
End-of-Life Recycling
The recycling of solar panels is becoming increasingly important as the industry grows. Efforts are being made to develop efficient recycling methods to recover valuable materials and minimize waste.
Energy SourceCarbon FootprintEnvironmental ImpactTraditional ElectricityHighSignificant greenhouse gas emissionsSolar EnergyLowMinimal environmental impact during operation
3. Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-term Savings
Evaluating the cost of solar installation against traditional electricity expenses is essential for homeowners considering a switch to renewable energy. The financial aspect of this decision involves a complex analysis of initial costs, ongoing expenses, and potential savings.
3.1 Upfront Costs of Solar Installation
The initial investment for solar energy systems includes the cost of solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and installation labor. While the upfront cost can be substantial, it's essential to consider the long-term benefits and potential return on investment.
For instance, the average cost of a solar panel system in the United States ranges from $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives. However, prices can vary based on the system size, equipment quality, and installation company.
3.2 Traditional Electricity Billing Structure
Traditional electricity billing is based on the amount of electricity consumed, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The cost per kWh varies by region and utility company, with average rates ranging from 10 to 20 cents per kWh.
In contrast, solar energy allows homeowners to generate their own electricity, potentially reducing their reliance on the grid and lowering their utility bills.
3.3 Return on Investment Timeline
The return on investment (ROI) for solar energy systems depends on several factors, including the initial cost, local electricity rates, and available incentives. Typically, homeowners can expect to break even on their investment within 5 to 10 years.
3.4 Financial Incentives and Tax Credits
Various financial incentives and tax credits can help offset the initial cost of solar energy systems. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront expense and improve the ROI.
Federal Tax Credits
The federal government offers a tax credit for solar energy systems, allowing homeowners to claim a percentage of the installation cost as a credit against their tax liability.
State and Local Incentives
In addition to federal tax credits, many states and local governments offer their own incentives, such as rebates, property tax exemptions, and performance-based incentives.
By understanding the costs associated with solar energy and traditional electricity, homeowners can make informed decisions about their energy choices. With the potential for long-term savings and environmental benefits, solar energy is an attractive option for those looking to reduce their energy expenses.
4.Reliability and Consistency Factors
Solar energy's effectiveness is heavily influenced by several reliability and consistency factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for evaluating its viability as a replacement for traditional electricity.
4.1 Weather Dependency of Solar Energy
One of the primary challenges facing solar energy is its dependency on weather conditions. Cloudy days and seasonal variations can significantly impact the amount of electricity generated.
Grid Reliability Issues
Traditional electricity grids face their own reliability issues, including infrastructure aging and peak demand management. Upgrading grid infrastructure is essential for supporting the integration of renewable energy sources.
4.2 Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage technologies play a vital role in mitigating the intermittency of solar energy. Effective solutions include:
- Advanced battery technologies
- Grid integration options
Battery Technologies
Advancements in battery technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, have improved the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of energy storage.
Grid Integration Options
Smart grid technologies enable better management of energy distribution, allowing for more efficient integration of solar energy into the grid.
Technology Benefits Challenges Lithium-ion Batteries High Efficiency, Cost-Effective Limited Lifespan, Resource Intensive Smart Grid Technologies Enhanced Energy Management, ScalabilityComplex Implementation, Cybersecurity Risks
By addressing these reliability and consistency factors, solar energy can become a more viable and reliable alternative to traditional electricity.
5. How to Evaluate Your Home's Solar Energy Potential
To harness the power of solar energy effectively, homeowners must first evaluate their property's solar potential. This assessment involves several critical factors that determine the feasibility and efficiency of a solar panel system.
5.1 Assessing Roof Orientation and Shading
The orientation and shading of your roof play a significant role in solar energy production. Ideally, roofs should face south to maximize sunlight exposure. Tools like solar pathfinder tools and online solar calculators can help assess shading issues.
Using Solar Pathfinder Tools
Solar pathfinder tools provide detailed analyses of your roof's solar potential by evaluating shading from trees, buildings, and other obstructions. These tools use advanced technology to give a clear picture of your roof's suitability for solar panels.
Online Solar Calculators
Online solar calculators offer a quick and easy way to estimate your home's solar potential. By inputting your location, roof size, and other relevant details, you can get an estimate of your potential solar energy production and savings.
5.2 Local Climate Considerations
Your local climate significantly impacts the effectiveness of your solar panel system. Areas with more sunlight throughout the year can generate more electricity. Understanding your local climate will help you make informed decisions about your solar energy system.
5.3 Space Requirements and Structural Factors
The amount of space available on your roof and its structural integrity are crucial factors. You'll need sufficient space for the solar panels and ensure your roof can support their weight. Consider factors like roof size, condition, and any potential obstructions.
5.4 Local Regulations and HOA Restrictions
Before installing solar panels, it's essential to check local regulations and HOA restrictions. Some areas have specific rules regarding the installation of solar energy systems, so it's crucial to comply with these regulations to avoid any issues.
By carefully evaluating these factors, homeowners can make informed decisions about their solar energy potential and enjoy the benefits of renewable energy.
- Assess your roof's orientation and shading.
- Use solar pathfinder tools and online solar calculators.
- Consider your local climate and its impact on solar energy production.
- Evaluate space requirements and structural factors.
- Check local regulations and HOA restrictions.
6.Step-by-Step Guide to Transitioning to Solar Energy
The journey to solar energy involves several key steps that, when followed, can lead to a successful transition. Homeowners must be well-informed to make the most out of their solar investment.
6.1Researching and Selecting Solar Installers
Choosing the right solar installer is crucial. Homeowners should start by checking credentials and reviews to ensure they're hiring a reputable company.
Checking Credentials and Reviews
Look for installers certified by organizations like the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP). Reading reviews on platforms like Yelp or Google can provide insights into the installer's work quality and customer service.
Getting Multiple Quotes
It's advisable to get quotes from at least three different solar installers. This allows homeowners to compare prices, services, and equipment quality.
6.2 Understanding Solar Proposals and Financing Options
Once you have selected potential installers, the next step is to understand their proposals and the financing options available.
Solar proposals should detail the system's size, equipment, costs, and expected energy production. Financing options can include outright purchase, loans, leases, or power purchase agreements (PPAs).
6.3 Navigating Permits and Utility Agreements
Before installation begins, homeowners must secure the necessary permits and enter into agreements with their utility company.
Permits vary by location but typically include building and electrical permits. Utility agreements may involve net metering contracts, which dictate how excess energy is handled.
6.4 Installation Process and Timeline
The installation process typically takes a few days to a few weeks, depending on the system's complexity and size.
Pre-Installation Home Preparations
Homeowners should clear the installation area of obstacles and ensure access to the roof or ground where the solar panels will be installed.
What to Expect During Installation
During installation, homeowners can expect the solar installer to mount the panels, install an inverter, and connect the system to the electrical panel.
 StepDescriptionTimelineResearch and SelectionResearching and selecting a solar installer1-2 weeksProposal and FinancingReviewing proposals and securing financing1-3 weeksPermits and AgreementsObtaining necessary permits and utility agreements2-6 weeksInstallationActual installation of the solar energy system1-3 weeks
StepDescriptionTimelineResearch and SelectionResearching and selecting a solar installer1-2 weeksProposal and FinancingReviewing proposals and securing financing1-3 weeksPermits and AgreementsObtaining necessary permits and utility agreements2-6 weeksInstallationActual installation of the solar energy system1-3 weeks
Transitioning to solar energy requires careful planning and execution, but with the right guidance, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of renewable energy and reduced energy costs.
7. Maintenance Requirements Comparison
Understanding the maintenance needs of solar energy versus traditional electricity is crucial for homeowners. Both systems have different requirements when it comes to upkeep and ensuring optimal performance.
7.1 Solar Panel Maintenance Schedule
Maintaining solar panels is relatively straightforward. Regular cleaning and performance monitoring are key to ensuring they operate efficiently.
Cleaning Procedures
Solar panels should be cleaned periodically to remove dirt and debris that can reduce their efficiency. Use a soft brush or cloth and mild detergent to avoid damaging the panels.
Performance Monitoring
Monitoring the performance of your solar panel system is essential to identify any issues early. Check your system's monitoring software regularly for any drops in energy production.
7.2 Traditional Electrical System Upkeep
Traditional electrical systems require more complex maintenance, including checking and replacing worn-out components.
7.3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
Troubleshooting for solar energy systems typically involves checking for shading issues or panel damage. For traditional electrical systems, troubleshooting can be more complex, involving circuit breakers, wiring, and other components.
8. Grid Connection vs. Off-Grid Solar Solutions
Understanding the differences between grid-connected and off-grid solar solutions is essential for making an informed decision about your energy needs.
8.1 How Grid-Tied Systems Work
Grid-tied solar systems are connected to the utility grid, allowing homeowners to use solar energy while still having access to traditional electricity when needed. This setup is beneficial for those who want to reduce their reliance on the grid without completely disconnecting from it.
Net Metering Explained
Net metering is a crucial aspect of grid-tied systems. It allows homeowners to generate their own electricity and export any surplus to the grid. The excess energy is then credited against the energy consumed from the grid, reducing the overall electricity bill.
Selling Power Back to Utilities
In addition to net metering, many utility companies offer the option to sell excess power back to them. This can provide an additional income stream for homeowners with solar installations.
 8.2 Battery Storage Implementation
8.2 Battery Storage Implementation
Battery storage systems are becoming increasingly popular as they allow homeowners to store excess energy generated by their solar panels for later use. This is particularly useful during power outages or at night.
8.3 Complete Off-Grid System Requirements
Off-grid solar systems require a more comprehensive setup, including a larger solar array, battery storage, and often a backup generator. These systems are ideal for remote locations where grid connection is not available or reliable.
Sizing Your System
Sizing an off-grid solar system correctly is critical to ensure it meets your energy needs. This involves calculating your daily energy consumption and determining the appropriate size of the solar array and battery bank.
Backup Power Solutions
Backup power solutions, such as generators, are often included in off-grid systems to provide power during extended periods of low sunlight. These solutions ensure a reliable energy supply.
FeatureGrid-Tied SystemsOff-Grid SystemsGrid ConnectionYesNoBattery StorageOptionalRequiredBackup PowerNot RequiredOften Included
As highlighted by a study on renewable energy systems, "the choice between grid-tied and off-grid solar solutions depends on various factors including location, energy needs, and budget." Understanding these factors is key to making the right choice for your solar energy needs.
9. Making the Switch: Real-World Solar Energy Success Stories
Real-world examples of homeowners who have made the switch to solar energy demonstrate its potential for long-term savings and environmental benefits. Homeowners across the United States are embracing solar energy, and their success stories are a testament to its advantages.
9.1 Residential Case Studies
Several homeowners have successfully transitioned to solar energy, enjoying significant reductions in their energy bills. For instance, a family in California installed a solar panel system on their home, reducing their energy bills by over 50%. The initial investment was recouped within five years, and they now enjoy nearly free electricity.
Another example is a homeowner in New York who installed a solar energy system with battery storage. During a recent power outage, the system provided backup power, ensuring the homeowner's home remained lit and comfortable. This experience highlighted the value of energy independence that solar energy can provide.
9.2 Common Challenges and Solutions
While transitioning to solar energy can be straightforward, some homeowners face challenges. Common issues include roof shading, high upfront costs, and navigating local regulations. However, many of these challenges can be mitigated with proper planning and professional guidance.
For example, a homeowner in a shaded area can opt for solar panels with higher efficiency ratings or consider ground-mounted solar installations. Financing options and incentives can also help alleviate the upfront costs.
"We were surprised by how easy it was to install solar panels on our home. The process was smooth, and the results have been fantastic." - John D., Solar Homeowner
9.3 Unexpected Benefits Reported by Homeowners
Homeowners who have switched to solar energy often report unexpected benefits, such as increased property values and improved energy independence. Some homeowners have even reported reductions in their homeowners' insurance premiums due to the added value and security of solar energy systems.
As the adoption of solar energy continues to grow, it is clear that the benefits extend beyond just cost savings. Homeowners are experiencing a new level of energy freedom and contributing to a more sustainable future.
10. Conclusion: Making the Right Energy Choice for Your Needs
As we've explored throughout this article, the decision between solar energy and traditional electricity hinges on several key factors, including environmental impact, cost, reliability, and personal energy needs. Understanding the solar energy benefits is crucial in making an informed energy choice.
Transitioning to solar energy can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and provide long-term savings on energy bills. While the initial investment may seem daunting, the return on investment and available financial incentives can make making the switch more feasible than ever.
Before deciding, it's essential to evaluate your home's solar potential, considering factors like roof orientation, local climate, and space requirements. By doing so, you can determine the best approach for your energy needs, whether that's a grid-tied system or an off-grid solution.
Ultimately, the right energy choice depends on your specific circumstances and priorities. By weighing the pros and cons of solar energy and traditional electricity, you can make a decision that aligns with your values and budget. Take the first step towards a more sustainable energy future today.
👉If you're ready to explore solar more closely and see how it could fit your lifestyle, I recommend starting with my full beginner's guide: Solar Power Made Simple
11.FAQ
Q : What is the main difference between solar energy and traditional electricity?
A: The primary difference lies in their generation sources; traditional electricity is often generated from fossil fuels, nuclear, and hydroelectric power, whereas solar energy is harnessed from the sun's rays using photovoltaic panels.
Q : How does solar energy work?
A: Solar energy works through the photovoltaic effect, where solar panels convert sunlight into electrical energy. The panels are made of semiconductor materials that release electrons when exposed to sunlight, generating an electric current.
Q : What are the environmental benefits of solar energy compared to traditional electricity?
A: Solar energy offers several environmental benefits, including a significant reduction in carbon footprint, as it produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants. In contrast, traditional electricity generation, particularly from fossil fuels, contributes to climate change and air pollution.
Q : What are the upfront costs associated with installing solar energy systems?
A : The upfront costs include the purchase and installation of solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and other necessary equipment, as well as labor costs. These costs can vary widely depending on the system's size, quality, and installer.
Q: Are there financial incentives available for homeowners who switch to solar energy?
A : Yes, there are various financial incentives, including federal tax credits, state and local incentives, and utility company rebates. These incentives can help offset the initial investment in solar energy systems.
Q : How do weather conditions affect the reliability of solar energy?
A: Solar energy generation is dependent on weather conditions, with sunlight being the primary requirement. Cloudy days and shading can reduce energy production, but advancements in technology and energy storage solutions are mitigating these challenges.
Q: What is the maintenance schedule for solar panels?
A: Solar panels require minimal maintenance, with cleaning recommended periodically to ensure optimal performance. Monitoring the system's performance is also crucial to identify any potential issues early.
Q: Can I go off-grid with solar energy, and what does it entail?
A: Yes, it is possible to go off-grid with solar energy by installing a complete off-grid system that includes solar panels, battery storage, and sometimes a backup generator. Sizing the system correctly and considering energy efficiency are key to a successful off-grid setup.
Q: How do grid-tied solar systems work, and what is net metering?
A: Grid-tied solar systems generate electricity and supply it to the grid, offsetting the homeowner's energy consumption. Net metering allows homeowners to sell excess energy back to the utility company, receiving credits on their electricity bills.
Q: What are the common challenges faced by homeowners when transitioning to solar energy?
A: Common challenges include assessing the home's solar potential, navigating local regulations and HOA restrictions, selecting a reliable solar installer, and understanding financing options and available incentives.