“Step-by-Step: How to Plan Your First Home Solar Installation”
Planning a home solar installation can seem daunting, but with a clear guide, it can be a straightforward process. As homeowners consider renewable energy sources, solar planning becomes increasingly important.
 By harnessing the power of the sun, homeowners can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and lower their energy bills. A well-planned solar installation can also increase a home's value and contribute to a cleaner environment.
By harnessing the power of the sun, homeowners can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and lower their energy bills. A well-planned solar installation can also increase a home's value and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the benefits of home solar energy
- Learn how to assess your home's solar potential
- Discover the steps involved in solar planning
- Find out how to choose the right solar installation equipment
- Understand the importance of maintenance and monitoring
1) The Benefits of Going Solar at Home
Solar energy offers a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. As homeowners look for ways to reduce their environmental footprint and energy bills, solar power is becoming an increasingly attractive option.
1.1)Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of solar energy is its potential to reduce carbon emissions. By harnessing energy from the sun, homeowners can significantly decrease their reliance on fossil fuels, thereby lowering their carbon footprint.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, solar energy is becoming increasingly cost-competitive with fossil fuels, making it a viable option for many households.
1.2) Long-term Financial Savings and ROI
In addition to its environmental benefits, solar energy can also provide substantial long-term financial savings.
Homeowners who install solar panels can expect to save on their energy bills, as the energy generated by the solar panels is free. Moreover, solar panels can increase a home's value, providing a return on investment for homeowners.
1.3) Energy Independence and Security
Solar energy also offers homeowners greater energy independence and security. By generating their own energy, homeowners are less susceptible to fluctuations in energy prices and less dependent on the grid.
This can be particularly beneficial during power outages or natural disasters, when traditional energy sources may be unavailable.
2) Assessing Your Home's Solar Potential
Assessing your home's solar potential involves several key factors that determine its suitability for solar panels. A thorough evaluation is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of your solar installation.
2.1) Evaluating Roof Orientation and Angle
The orientation and angle of your roof significantly impact the performance of your solar panels. Ideal roof conditions can boost energy production.
Ideal Directions and Pitches
A south-facing roof with a moderate pitch is generally considered optimal for solar installations. However, variations can still yield excellent results.
Working with Non-Optimal Roof Conditions
Even if your roof isn't ideally oriented, solar panels can still be effective. Adjustments in panel placement and tilt can help optimize energy production.
2.2) Calculating Sun Exposure and Shading Analysis
A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that roof orientation and shading significantly impact solar panel efficiency. Conducting a shading analysis can help identify potential obstructions.
Factor Ideal Condition Impact on Solar Potential Roof Orientation South-facing High Roof Angle Moderate pitch High Shading Minimal shading High
2.3) Determining Available Roof Space and Structural Integrity
It's essential to assess the available roof space and ensure that your roof can support the weight of solar panels. A professional evaluation can help determine your home's solar potential.
3) Analyzing Your Current and Future Energy Needs
Analyzing your energy needs is a vital step in determining the right size and type of solar installation for your home. To do this effectively, you need to understand your current energy usage patterns and anticipate future demands.
3.1) Reviewing Past Utility Bills and Usage Patterns
The U.S. Department of Energy suggests analyzing past utility bills to understand energy usage patterns. By reviewing your past bills, you can identify your average energy consumption and peak usage periods. This information is crucial for sizing your solar installation correctly.
3.2) Identifying Peak Consumption Periods
Identifying peak consumption periods helps you understand when you use the most energy. This could be during hot summer afternoons when your air conditioning is running or during cold winter mornings when your heating system is working hard. By understanding these patterns, you can optimize your solar installation to meet your energy needs during these peak periods.
3.3) Accounting for Future Changes
It's also essential to consider future changes that might impact your energy needs, such as purchasing an electric vehicle or adding to your home. These changes can significantly increase your energy consumption, and your solar installation should be designed to accommodate these future demands. Planning ahead ensures that your solar installation remains effective and efficient over its lifespan.
- Review past utility bills to understand energy usage patterns.
- Identify peak consumption periods to optimize your solar installation.
- Consider future changes that might impact your energy needs.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your solar installation is tailored to your specific energy needs, both now and in the future.
4) Setting Realistic Goals for Your Solar Installation
A well-planned solar installation starts with setting realistic goals. Homeowners must consider their energy needs, budget constraints, and long-term objectives to maximize the benefits of solar energy.
According to a survey by the Solar Energy Industries Association, setting clear goals is crucial for a successful solar installation. This involves evaluating your energy independence requirements, budget parameters, and both short-term and long-term objectives.
4.1) Partial vs. Complete Energy Independence
Homeowners can choose between partial and complete energy independence. While complete energy independence offers maximum savings and self-sufficiency, partial independence can be a more affordable and practical starting point.
4.2) Budget Parameters and Constraints
Understanding your budget is critical. Consider not only the upfront costs but also potential financing options and incentives that can offset expenses.
4.3) Short-term vs. Long-term Objectives
It's essential to balance short-term needs with long-term goals. Consider factors like potential home additions, changes in energy usage, or the adoption of electric vehicles.
Key considerations:
- Assess your current energy usage and future needs.
- Evaluate your budget and financing options.
- Determine your desired level of energy independence.
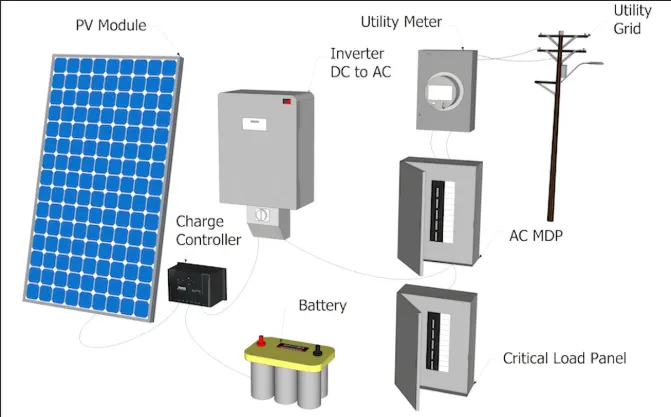
5) Understanding Solar System Components
A solar system installation comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in harnessing and converting solar energy.
Understanding these components is essential for homeowners to make informed decisions about their solar installation.
5.1) Solar Panel Types and Efficiency Ratings
Solar panels are the most visible component of a solar energy system. They come in different types, each with its own efficiency rating.
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline vs. Thin Film
- Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency rates and sleek appearance.
- Polycrystalline panels offer a cost-effective option with slightly lower efficiency rates.
- Thin Film panels are less common but offer flexibility and a unique aesthetic.
Power Output and Degradation Rates
When selecting solar panels, it's crucial to consider their power output and degradation rates. Higher efficiency panels may cost more upfront but can provide better long-term savings.
5.2) Inverter Options
Inverters are critical for converting DC power generated by solar panels into AC power usable in homes.
There are several types of inverters available, including:
- String Inverters: Cost-effective and widely used.
- Microinverters: Offer panel-level optimization and monitoring.
- Power Optimizers: Provide a compromise between string inverters and microinverters.
5.3) Battery Storage Solutions
Battery storage allows homeowners to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during power outages. Popular battery storage solutions include lithium-ion batteries.
5.4) Mounting Systems and Hardware
The mounting system secures the solar panels to the roof or ground. It's essential to choose a durable mounting system that can withstand various weather conditions.
By understanding the different components of a solar energy system, homeowners can better navigate the installation process and ensure their system meets their energy needs.
6) Calculating the Ideal Solar Installation Size
Calculating the ideal solar installation size involves understanding your energy needs and usage patterns. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory provides valuable tools and resources to help homeowners determine the appropriate size for their solar installation based on their energy requirements.
6.1) Determining Kilowatt Requirements Based on Usage
To determine the kilowatt requirements, review your past utility bills to understand your average energy consumption.
This analysis will help you identify the size of the solar installation needed to meet your energy demands.
6.2) Panel Quantity and Arrangement Considerations
The number and arrangement of solar panels depend on several factors, including available roof space, panel efficiency, and desired energy output. A professional solar installer can help optimize panel placement for maximum energy production.
 6.3) Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid System Design
6.3) Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid System Design
Your solar installation size will also depend on whether you're opting for a grid-tied or off-grid system. Grid-tied systems are connected to the utility grid, while off-grid systems require battery storage to provide energy independence.
6.4) Expansion Potential for Future Needs
When designing your solar installation, consider potential future energy needs, such as adding electric vehicles or home expansions. A scalable system can be designed to accommodate these future requirements, ensuring your solar installation remains efficient and effective.
7) Navigating Solar Installation Costs and Financing
As homeowners consider solar energy, navigating the costs and financing options becomes essential.
The initial investment in solar panels and associated equipment can be significant, but understanding the various expenses and available incentives can make the transition to solar energy more manageable.
7.1) Breaking Down Installation Expenses
The total cost of solar installation includes several components.
Equipment costs are a major part, encompassing solar panels, inverters, and mounting hardware.
Labor and installation fees also contribute significantly to the overall expense.
Equipment Costs
Equipment costs vary based on the quality and efficiency of the solar panels and other system components. High-efficiency panels, while more expensive, can provide better long-term value.
Labor and Installation Fees
Labor costs can differ depending on the complexity of the installation and local labor rates. It's essential to get quotes from multiple installers to compare prices.
7.2) Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a significant incentive for homeowners. It allows you to deduct a substantial percentage of your solar installation costs from your federal taxes. As noted by the Solar Energy Industries Association, "The ITC is one of the most important federal incentives for solar energy."
"The ITC has been instrumental in driving the growth of solar energy in the United States."
Solar Energy Industries Association
7.3) State and Local Incentive Programs
In addition to the federal tax credit, many states and local governments offer their own incentive programs.
These can include rebates, tax credits, and other benefits that can significantly reduce the cost of solar installation.
7.4) Financing Options: Loans, Leases, and PPAs
Homeowners have several financing options to consider. Loans allow you to own the system outright, while leases and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) provide alternatives that require little to no upfront costs.
- Loans: Allow ownership and potential tax benefits
- Leases: Lower upfront costs, fixed monthly payments
- PPAs: Pay for the electricity generated, not the equipment
7.5) Calculating Payback Period and ROI
Understanding the payback period and return on investment (ROI) is crucial for evaluating the financial viability of your solar installation.
By analyzing your energy savings and the costs associated with your solar system, you can determine how long it will take to recoup your investment.
By carefully considering these factors and exploring available incentives, homeowners can make informed decisions about their solar installation, ensuring a sound investment in renewable energy.
8) Researching and Selecting Qualified Solar Providers
To ensure a smooth and efficient solar installation, it's essential to research potential providers thoroughly. A qualified solar provider can make a significant difference in the overall success of your project.
8.1) Verifying Credentials and Certifications
One of the first steps in selecting a solar provider is to verify their credentials.
Look for certifications from reputable organizations such as the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP).
This certification indicates that the provider has met certain standards in the industry.
8.2) Evaluating Experience and Track Record
Assess the provider's experience by reviewing their past projects and customer testimonials. A provider with a strong track record is more likely to deliver a successful installation.
8.3) Reading Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Customer reviews can provide valuable insights into a provider's reliability and quality of service. Check online review platforms and ask for references to get a well-rounded view.
8.4) Comparing Quotes, Warranties, and Service Agreements
When comparing solar providers, it's crucial to evaluate their quotes, warranties, and service agreements. A detailed comparison can help you make an informed decision.
9) Understanding Permitting and Regulatory Requirements
Navigating the complex world of solar installation requires a thorough understanding of the various permitting and regulatory requirements. Homeowners must comply with a range of regulations to ensure their solar installation is done correctly and legally.
9.1) Local Building Codes and Permit Processes
Local building codes and permit processes are critical components of solar installation. The Interstate Renewable Energy Council (IREC) provides valuable resources to help navigate these requirements. Homeowners should check with their local government to understand the specific codes and permits needed.
9.2) Homeowners Association (HOA) Restrictions
For those living in areas with HOA restrictions, it's essential to review the community's rules and regulations regarding solar installations. Some HOAs may have specific requirements or limitations on the size, placement, or type of solar panels allowed.
 9.3) Utility Interconnection Requirements
9.3) Utility Interconnection Requirements
Utility interconnection requirements are another crucial aspect. Homeowners must ensure their solar installation meets the utility company's standards for connecting to the grid. This includes complying with specific technical and safety requirements.
9.4) Insurance Considerations
Finally, homeowners should review their insurance policies to understand how their solar installation will be covered. Some insurance providers may have specific requirements or recommendations for insuring solar panels.
As "The solar industry is rapidly evolving, and staying informed about regulatory requirements is key to a successful installation." By understanding and complying with these regulations, homeowners can ensure a smooth and successful solar installation experience.
10) Creating a Timeline for Your Solar Installation Project
Creating a timeline for your solar installation project is crucial for a smooth transition to renewable energy. A typical solar installation project can take several months from initial planning to activation. Understanding the various stages involved and their respective timelines can help homeowners plan and prepare for the process.
The solar installation process can be broken down into several key phases. First, there's the Research and Planning Phase, which typically lasts 2-3 months. During this period, homeowners assess their energy needs, evaluate their home's solar potential, and research potential solar providers.
10.1) Research and Planning Phase (2-3 months)
This phase involves reviewing past utility bills, identifying peak consumption periods, and determining the ideal solar installation size. Homeowners should also research and select qualified solar providers, comparing quotes, warranties, and service agreements.
10.2) Permitting and Approval Process (1-2 months)
Once the planning phase is complete, the next step is to obtain the necessary permits and approvals. This process can take 1-2 months, depending on local regulations and the complexity of the installation.
The actual installation is typically completed within 1-2 weeks. However, the overall timeline may vary depending on the installer's workload and the complexity of the project.
10.3) Installation and Connection Schedule (1-2 weeks)
During this phase, the solar installation team will mount the solar panels, install the inverter and other necessary equipment, and connect the system to the grid.
10.4) Inspection and Activation (1-2 weeks)
After the installation is complete, the system must be inspected and activated. This involves verifying that the system meets local building codes and utility interconnection requirements.
By understanding these phases and their respective timelines, homeowners can better plan and manage their solar installation project. It's essential to work closely with your solar provider to ensure a smooth and efficient process.
11) Preparing Your Home for Solar Panel Installation
Before installing solar panels, it's crucial to prepare your home to ensure a smooth and efficient installation process. This preparation not only involves assessing your current energy needs but also evaluating your home's infrastructure to support the solar panel system.
11.1) Necessary Electrical System Upgrades
Ensuring that your home's electrical system is up to code is vital before installing solar panels.
This may involve upgrading your electrical panel to handle the additional power generated by the solar panels. An outdated or inadequate electrical system can lead to safety issues and inefficiencies in your solar energy system.
11.2) Roof Repairs or Reinforcement Requirements
Your roof must be in good condition to support the weight and installation of solar panels.
This might require repairs or reinforcements to ensure it can bear the load. A thorough inspection by a professional can identify any necessary work, ensuring your roof is ready for the solar panel installation.
11.3) Site Access Considerations for Installation Crews
Ensuring that installation crews have unobstructed access to your roof and electrical panel is crucial.
This means clearing any obstacles such as debris, overgrown vegetation, or tight spaces that could hinder the installation process.
11.4) Temporary Power Arrangements During Installation
In some cases, temporary power arrangements may be necessary during the installation process. This could involve planning for potential power outages or working with your installer to schedule the installation during periods of low energy usage.
By addressing these key areas, you can ensure that your home is properly prepared for solar panel installation, maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of your solar energy system.
12) Conclusion: Embracing Solar Energy for a Sustainable Future
As we've explored throughout this guide, transitioning to solar energy is a significant step towards a more sustainable future.
By understanding your home's solar potential, analyzing your energy needs, and carefully planning your solar installation, you can reap the benefits of renewable energy.
Solar energy not only reduces your carbon footprint but also provides long-term financial savings and energy independence.
With the right solar system components, financing options, and qualified solar providers, you can achieve a successful solar installation that meets your needs.
As you move forward with your solar journey, remember that careful planning and execution are crucial to maximizing the benefits of solar energy.
By doing so, you'll be contributing to a sustainable future while enjoying the advantages of renewable energy.
FAQ
Q: What are the benefits of going solar at home?
A: Going solar at home can reduce your carbon footprint, save on energy bills, and increase your energy independence. Solar panels can also increase your home's value and provide a return on investment.
Q: How do I assess my home's solar potential?
A: To assess your home's solar potential, evaluate your roof's orientation, angle, and sun exposure. Consider factors like shading, roof size, and structural integrity to determine if solar panels are suitable for your home.
Q: What factors should I consider when analyzing my current and future energy needs?
A: Review your past utility bills and usage patterns to understand your energy needs. Consider peak consumption periods, future changes like purchasing an electric vehicle or adding to your home, and how these factors may impact your energy usage.
Q: How do I determine the ideal solar installation size for my home?
A: To determine the ideal solar installation size, calculate your kilowatt requirements based on your energy usage. Consider panel quantity, system design, and potential for future expansion to ensure your solar installation meets your needs.
Q: What financing options are available for solar installations?
A: Financing options for solar installations include loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs). You can also take advantage of federal and state incentives, such as the Solar Investment Tax Credit, to make solar more affordable.
Q: How do I research and select a qualified solar provider?
A: To research and select a qualified solar provider, verify their credentials and certifications, evaluate their experience and track record, read customer reviews, and compare quotes, warranties, and service agreements.
Q: What are the typical costs associated with solar installation?
A: Solar installation costs include equipment costs, labor and installation fees, and other expenses. The total cost will depend on the size and complexity of your solar installation.
Q: How long does a solar installation project typically take?
A: A typical solar installation project can take several months from initial planning to activation, including research and planning, permitting and approval, installation, and inspection and activation.
Q: What are the permitting and regulatory requirements for solar installations?
A: Permitting and regulatory requirements for solar installations vary by location and include local building codes, homeowners association (HOA) restrictions, utility interconnection requirements, and insurance considerations.
Q: How do I prepare my home for solar panel installation?
A: To prepare your home for solar panel installation, ensure your electrical system is up to code, make any necessary roof repairs or reinforcements, and provide site access for installation crews. You may also need to make temporary power arrangements during the installation process.